Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) combines two different approaches for a practical and solution-focused therapy. The therapy is very active by nature, so you may be expected to take a proactive role within your treatment. This may include completing
tasks at home.
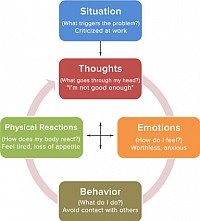
The idea behind CBT is that our thoughts and behaviours have an effect on each other. That by changing the way we think or behave in a situation, we can change the way we feel about life. The therapy examines learnt behaviours, habits and negative thought patterns with the view of adapting and turning them into a positive.
Unlike some other therapies, CBT is rooted in the present and looks to the future. While past events and experiences are considered during the sessions, the focus is more on current concerns. During a CBT session, your therapist will help you understand any negative thought patterns you have. You will learn how they affect you and most importantly, what can be done to change them.
Cognitive behavioural therapy looks at how both cognitive and behavioural processes affect one another and aims to help you get out of negative cycles. The emphasis on behavioural or cognitive approaches will depend on the issue you are facing. For example, if you are suffering from anxiety or depression, the focus may be on the cognitive approach. If you have a condition that causes unhelpful behaviour (such as obsessive compulsive disorder), the focus is likely to be the behavioural approach.
This type of therapy is particularly helpful for those with specific issues. This is because it is very practical (rather than insight-based) and looks at solving the problem. Some of the people that may benefit from cognitive behavioural therapy include:
- Those who suffer from depression and/or anxiety.
- People who are suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- People who are experiencing sleeping problems, such as insomnia.
- People who have a fear or phobia.
- Those who suffer from obsessive compulsive disorder.
- Those who want to change their behaviour.
In some cases, CBT is used for those with long-standing health problems, such as chronic pain or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). While the therapy cannot cure such physical ailments, it can help people cope emotionally with the symptoms and lower stress levels.